Renewable energy
The Advantages of Hokkaido
Hokkaido has the greatest potential for renewable energy in the country
In the aftermath of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, Hokkaido faced widespread network congestion issues, particularly with the cellular network, which acts as a lifeline for many people in this modern age. Hokkaido’s vulnerability to natural disasters became a topic of much discussion, and both the public and private sectors decided to work together to strengthen its telecommunications network.
After the earthquake, renewable energy such as solar power began to be introduced with the support of the Japanese government through measures such as FITs (feed-in tariffs). In 2018, Hokkaido was hit by a blackout after the Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, but now, its power grid has been strengthened significantly. This is due to the use of renewable energy in conjunction with the installation of the New Hokkaido-Honshu Link connecting Hokkaido to the mainland.
In addition, in order to begin introducing large-scale offshore wind power stations throughout Hokkaido, plans to install a Newer Hokkaido-Honshu Link and a new submarine power cable between Hokkaido and the mainland are underway.
In this manner, Hokkaido has been able to learn from the widespread natural disasters it has experienced to develop plans to address its vulnerabilities in both telecommunications and power.
Furthermore, as calls to reduce consumption of greenhouse gases like CO2 have risen in recent years. In response, the government announced their “Green Growth Strategy” in December 2020, a plan to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to virtually zero by 2050. With the expected increase of the public and private sectors’ investments in the introduction of renewable energy, it is essential to ensure that renewable energy is implemented to power the energy-hungry data centers being constructed.
To that end, Hokkaido’s cool climate can be harnessed to reduce the power needed for the cooling of data centers, and the construction and development of renewable energy power plants is underway on the island’s expansive tracts of open land. Hokkaido will be established as a supply base for renewable energy which can support a large number of data centers.

Renewable energy examples
-
 ReENE Zenibako Wind Farm: 34MW
ReENE Zenibako Wind Farm: 34MW
Source: Tokyu Land Corporation website -
 Shuparo Dam Power Station, Yubari: 28MW
Shuparo Dam Power Station, Yubari: 28MW
-
 SoftBank Tomatoh Abira Solar Park: 111MW
SoftBank Tomatoh Abira Solar Park: 111MW
Source: SB Energy Corp. website -
 Tomakomai Biomass Power Station 7MW
Tomakomai Biomass Power Station 7MW
Source: Tomakomai Biomass Power Co., Ltd. website
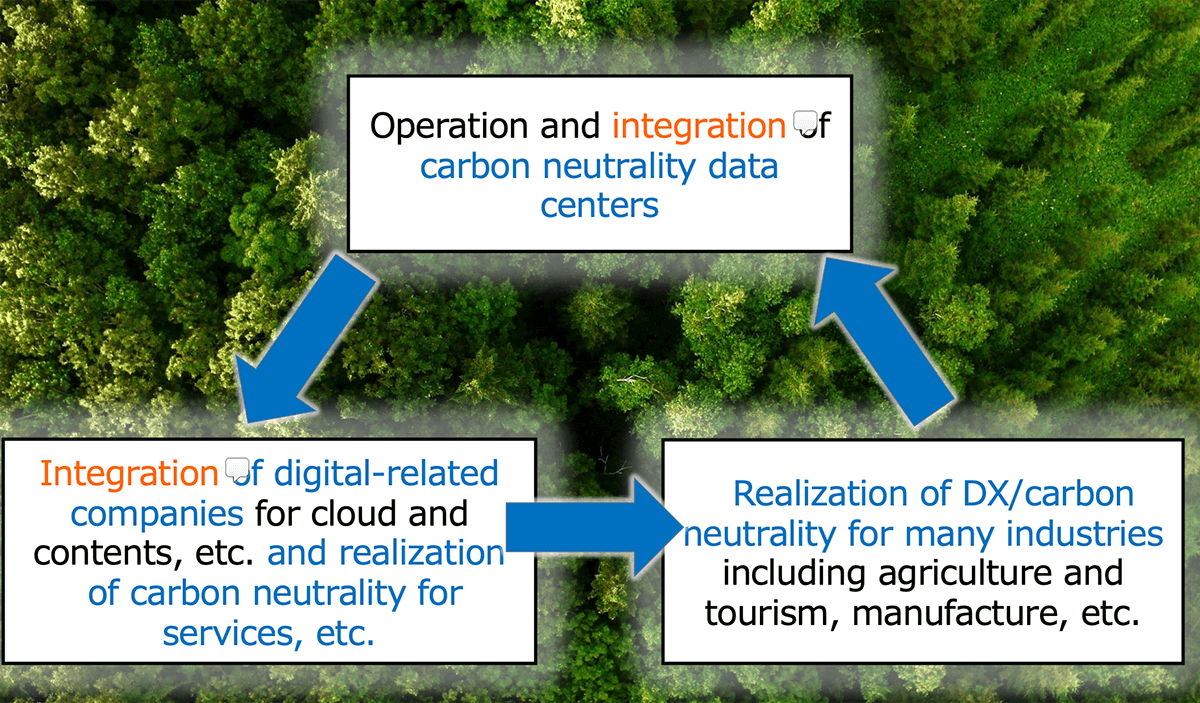
Digital×Carbon Neutrality: Using Hokkaido’s cool climate and vast renewable energy resources
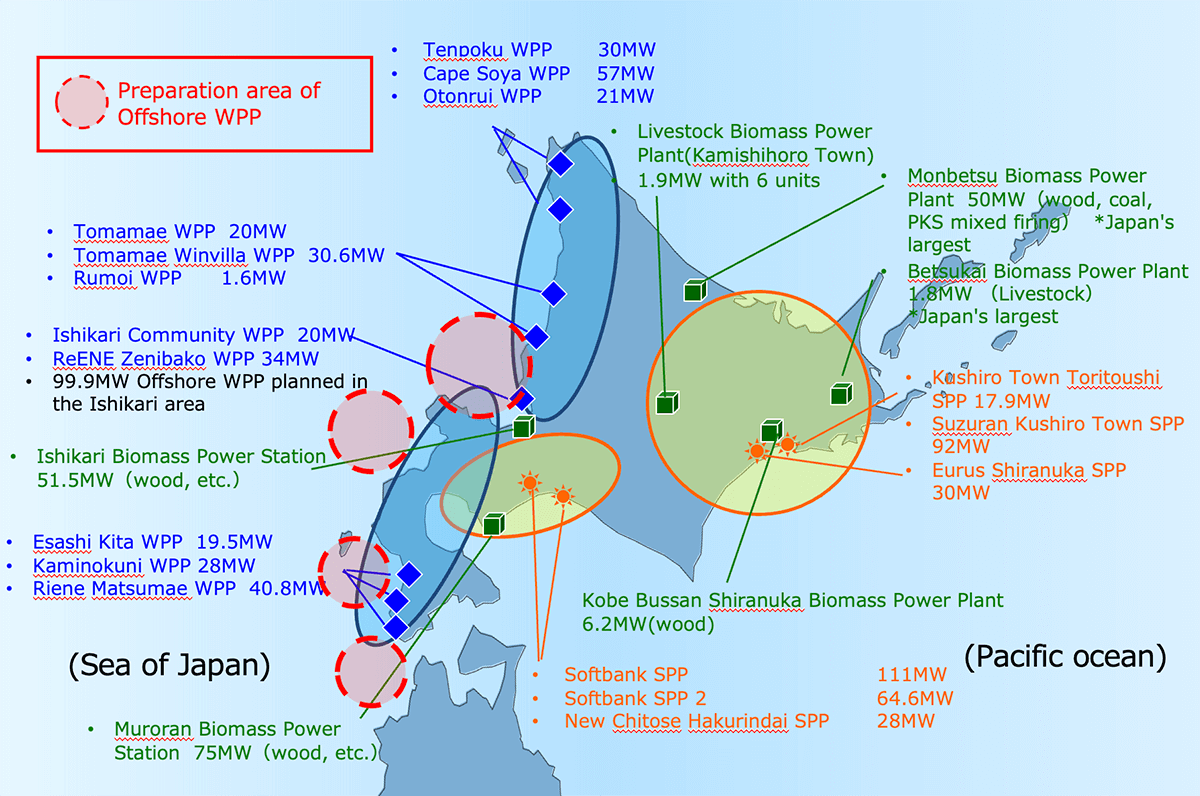
Status of Hokkaido’s main renewable energy resources
- Hokkaido has the most potential in Japan for wind power stations, small and medium-sized hydropower plants, and solar farms.
- Operation of large-scale offshore wind power stations will begin in 2030.
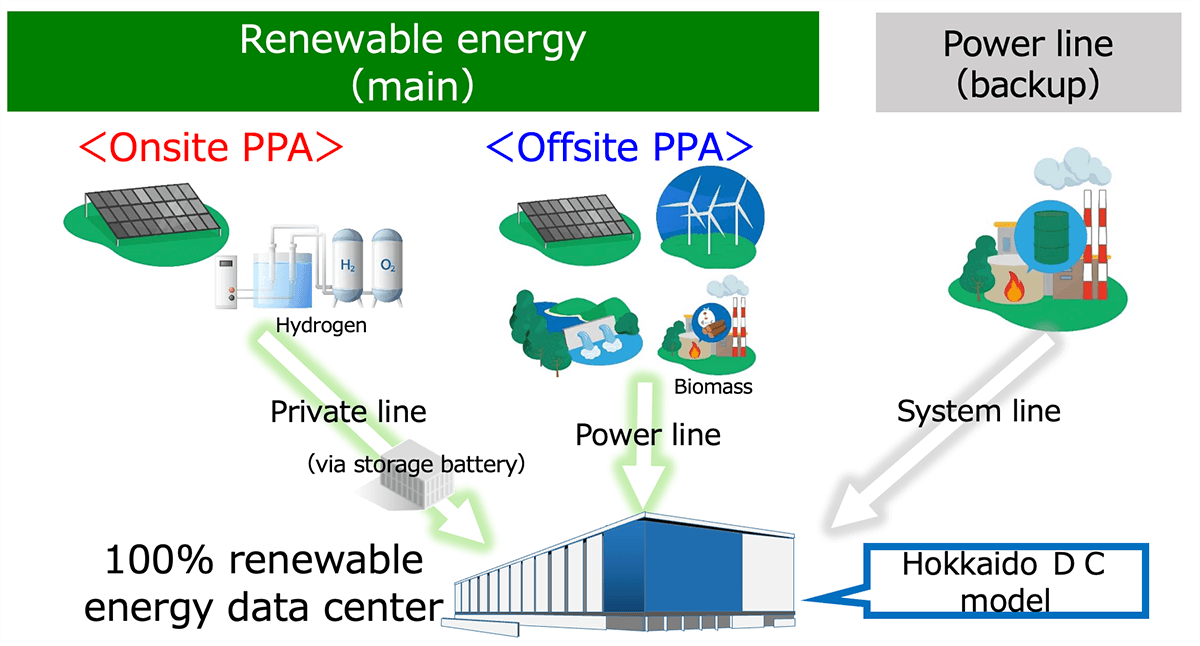
Building renewable energy supply solutions
- Hokkaido Electric Power Company and Tokyo-area energy companies are considering supply solutions via onsite and offsite PPA.
- We are aiming for 100% physical delivery of renewable energy using several different resources.
Solar Power (Mega Solar)
Positioning of Mega Solar Power Stations
Tomakomai and Kushiroshi, located on the Pacific Ocean, see less snowfall compared to other parts of Hokkaido. Thus, there is no drop in the daylight hours in the fall and winter and receive a constant amount of solar radiation throughout the year.Also, due to their proximity to areas with high power consumption and large transformer substations, and their vast plots of land for industrial sites, these locations have been chosen to house mega solar power stations.
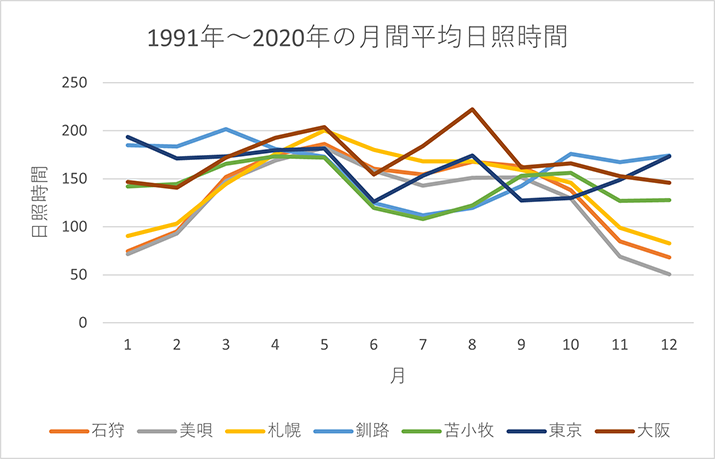 Average Daily Sunshine Duration per Month in 1991-2020.
Average Daily Sunshine Duration per Month in 1991-2020.
Main Mega-Solar Power Stations in Hokkaido
-
NameCompanyScale (MW)
-
Tomatoh Abira Solar Park 1SB Energy Corp.111
-
Tomatoh Abira Solar Park 2SB Energy Corp.64.6
-
Sharp Tomatoh no Mori Solar Power StationTomakomai Solar Energy LLC45.6
-
Sharp Tomakomai No. 3 Solar Power StationCrystal Clear Solar LLC38
-
Tomakomai Yufutsu Mega SolarTomakomai Yufutsu Solar Park LLC29.8
-
Hokkaido Tomakomai ProjectGreen Power Development Corporation of Japan38.4
-
Mitsui Fudosan Tomakomai Solar Power StationMitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd.23
-
Yufutsu Solar Power StationSolar Power Tomakomai Co., Ltd.15.2
-
Eurus Shiranuka Solar ParkEurus Energy Holdings Corporation30
-
Kushiro Town Toritoushi Wildland Solar Power PlantObayashi Clean Energy Corporation17.9
Wind Power
Projects and plans for wind power are increasing in northern and southern Hokkaido as well as the Ishikari area.
Ishikari city is setting its “Smart Energy” plan, which aims to make use of the renewable energy resources of the Ishikari Bay New Port Area. Wind from the Japan Sea constantly blows into Ishikari Bay year-round, making it well suited for wind power stations. In recent years, non-profit organizations such as Hokkaido Green fund and Community Wind Power have installed wind turbines with the help of the local community, and Green Power Investment Corporation is constructing a 100-megawatt offshore wind power station in the bay.
In addition, domestic and international companies have come together to develop a variety of plans for several-hundred-megawatt offshore wind power stations to be constructed in the sea beyond the bay. Various kinds of assessments are currently underway in southern Hokkaido and the Ishikari area.
Currently active wind power stations include Eurus Date Wind Farm (10MW [2MW×5 turbines], started operation in November 2011) and the Eurus Date Kogane Wind Farm (34MW [2MW×17 turbines], started operation in early 2017) in the Muroran/Date area.
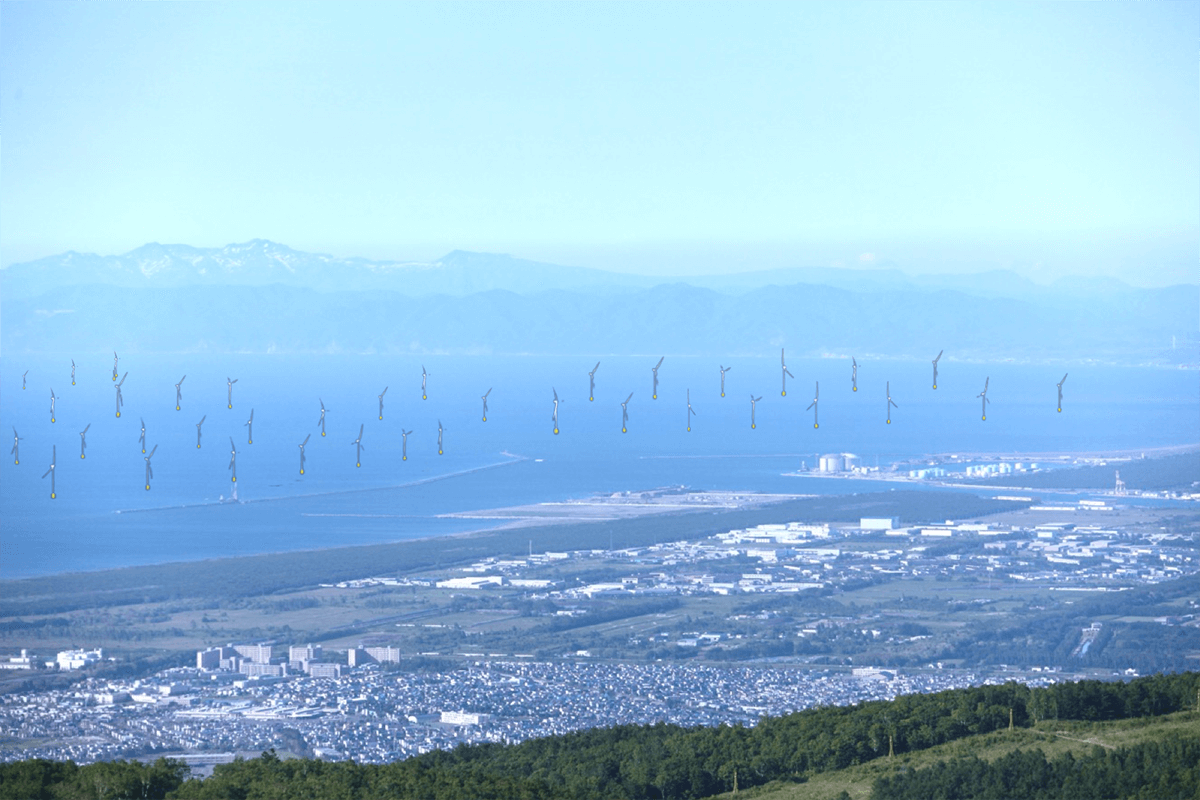 Panorama of Ishikari Bay after Installation of Offshore Wind Power Stations
Panorama of Ishikari Bay after Installation of Offshore Wind Power Stations
Provided by: Akio Hachinohe (partially rendered)
Plans for Large-Scale Offshore Wind Power Stations in the Sea
-
CompanyMaximum Output (MW)Area
-
Japan Renewable Energy Corporation1,000Ishikari are
-
Cosmo Eco Power Co., Ltd.1,000Ishikari area
-
Electric Power Development Co., Ltd.722Hiyama area
-
Hokkaido Offshore Wind Development GK585Shiribeshi area
Contact
-
Contact by Phone
Hokkaido Economic Affairs Bureau Industrial Promotion Division Location Promotion Section
011-204-5328(Japanese only)
-
Contact via Form




