Vision
Hokkaido:
A location in Asia with cool weather and few geopolitical risks
With the use of computers comes the generation of heat. To counteract this, data centers often consume a great amount of energy to cool its systems. However, as Hokkaido is a naturally cold region, its data centers can employ free cooling, a method of cooling which uses the air.
A Proposal from Hokkaido
Video message from Hokkaido’s governor, 2022
Video message from Hokkaido’s governor, 2024
Preparing to become a major hub for the digital
industry, becoming a growth engine
for domestic economics.
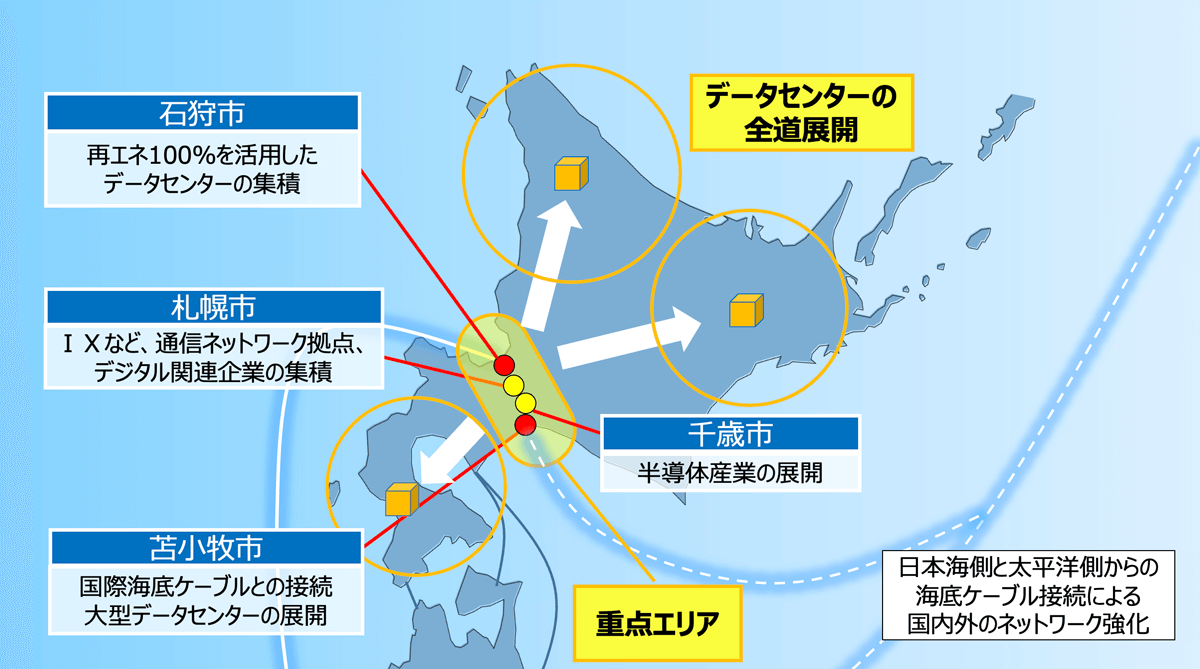
Making Hokkaido the place with the most data centers in Japan
In December 2020, the Japanese government announced the Green Growth Strategy, a plan to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to virtually zero by 2050.
In addition to its cool climate allowing for reduced energy consumption in data center cooling, Hokkaido has a vast amount of land. The construction of large-scale renewable energy power stations by both domestic and international companies will establish an environment in which renewable energy is readily available, giving Hokkaido the potential to attract many data centers going forward.
Based on these locational conditions, the Hokkaido government will propose locations suitable for data centers to data center operators, cloud service providers, developers, and investors both in Japan and overseas who are considering entering Hokkaido. The goal: to turn Hokkaido into a hotspot for data centers not only in Japan, but throughout Asia.
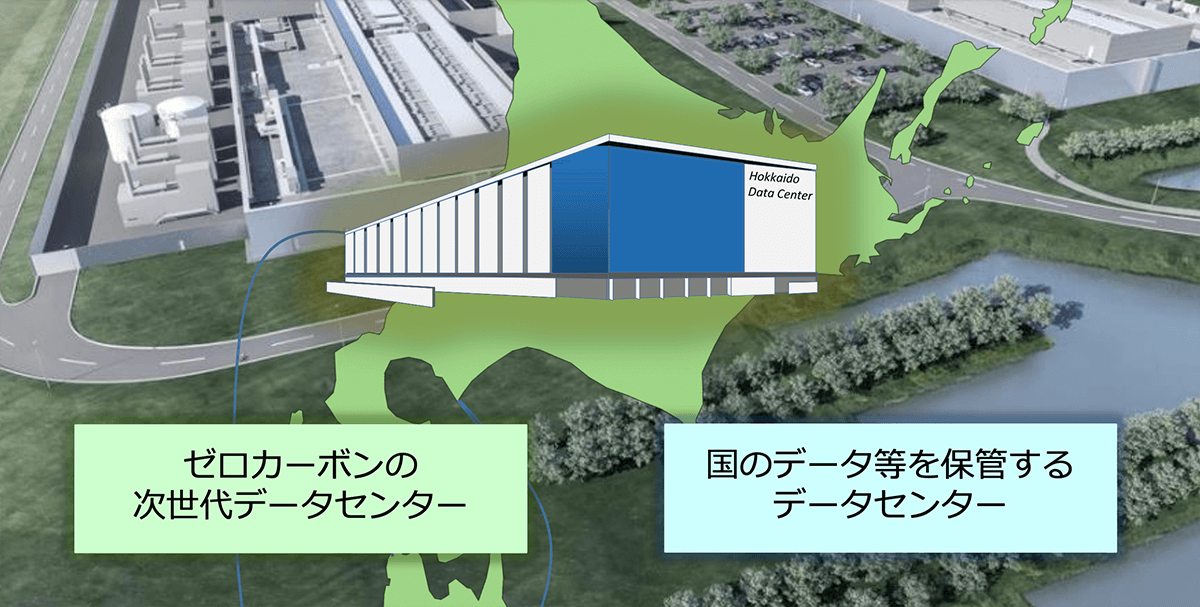 Background image source:Odense Data Center facebook
Background image source:Odense Data Center facebook
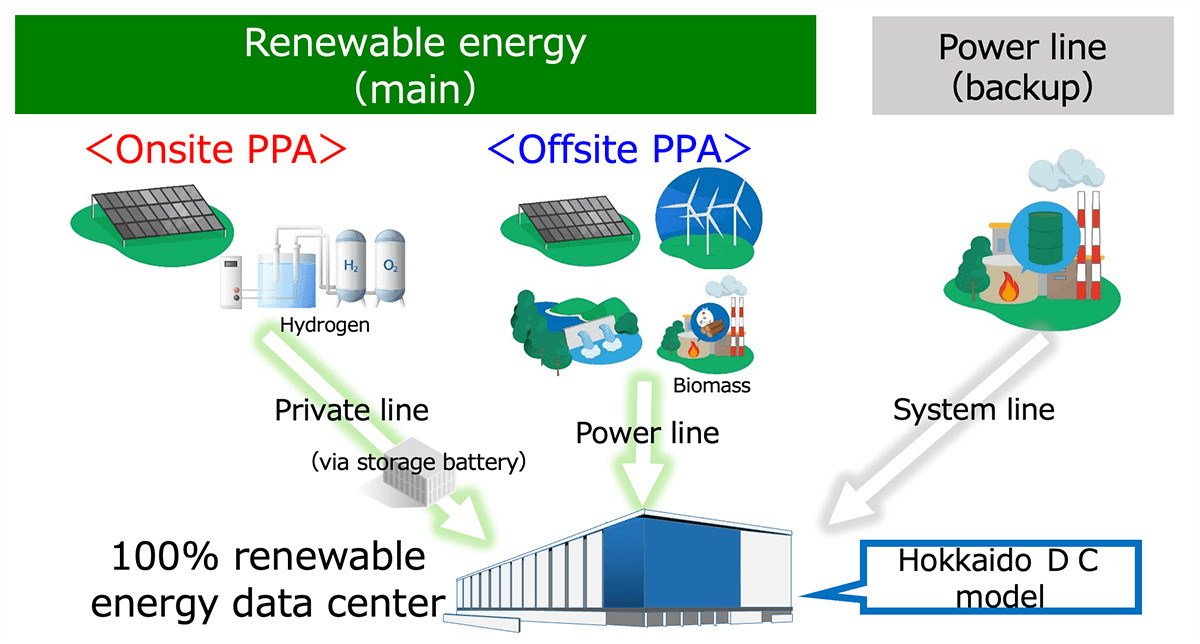
Efforts to Attract DCs: Hokkaido DC Model
- The Hokkaido government is proposing the Hokkaido DC Model, in which both onsite PPA and offsite PPA are used to deliver renewable energy to data centers.
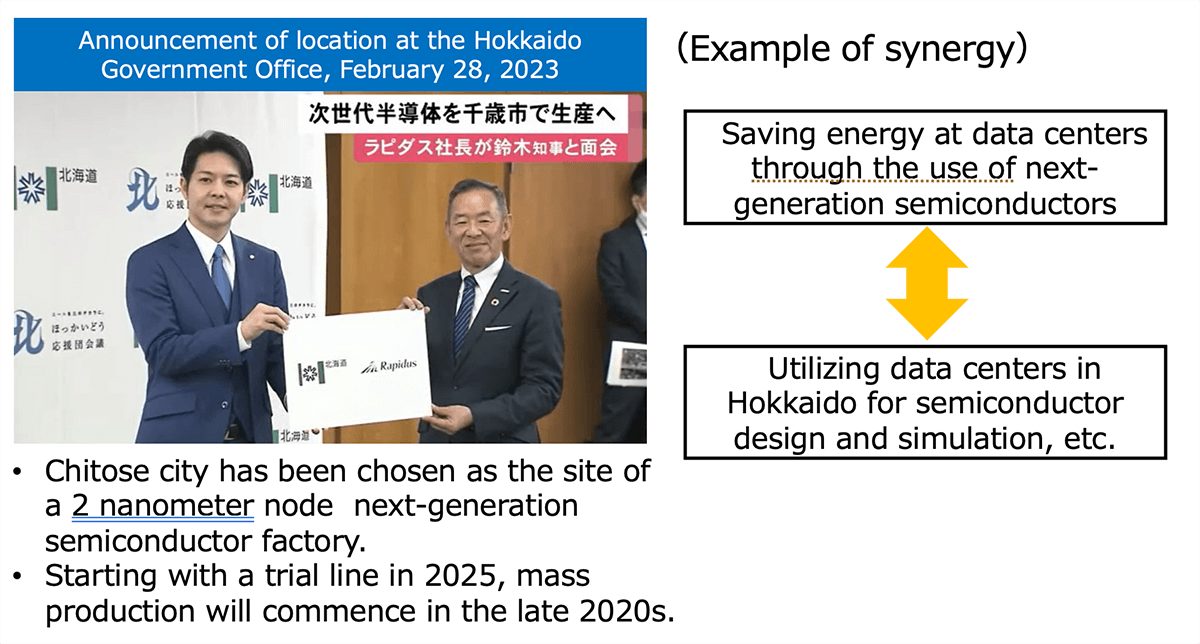
Cooperation with Semiconductor Companies
- In cooperation with semiconductor company Rapidus Corporation, who have announced a landing station in Chitose city, demonstrating maximum synergy in both digital industry hardware (semiconductors) and software (data centers).
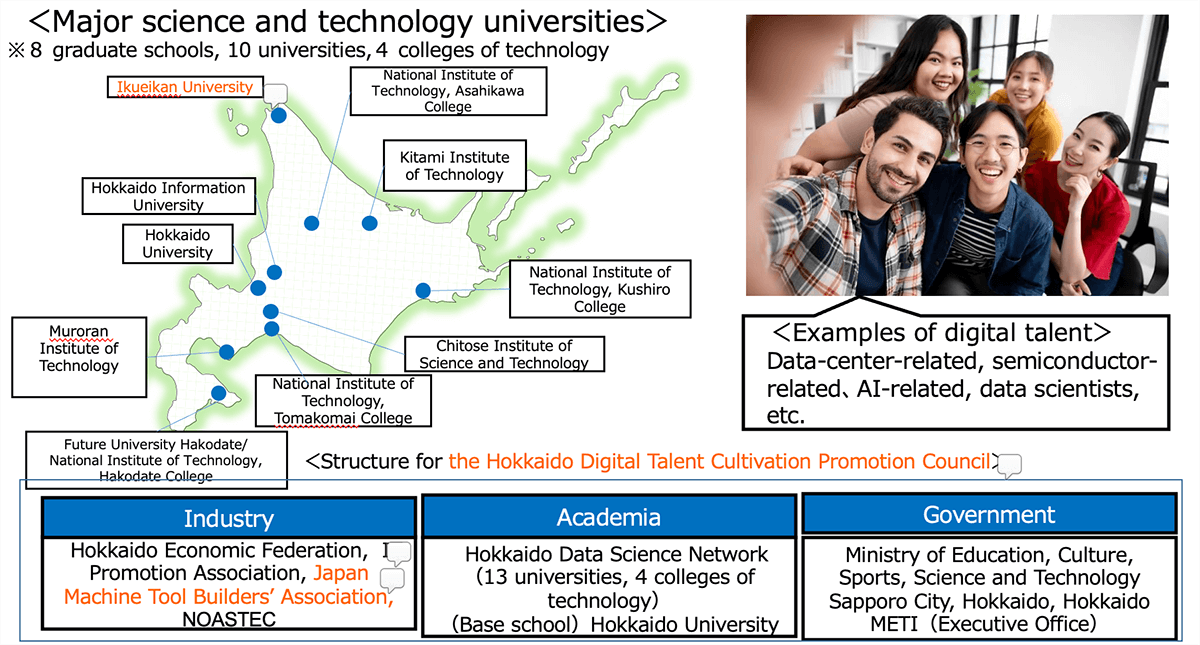
Training and Supply of Digital Talent
- The Hokkaido Digital Digital Talent Cultivation Promotion Council was launched on March 14, 2023 in cooperation with industry, academia and government.
- Cultivation and supply of talent who will support Hokkaido’s digital industry such as data-center related talent.
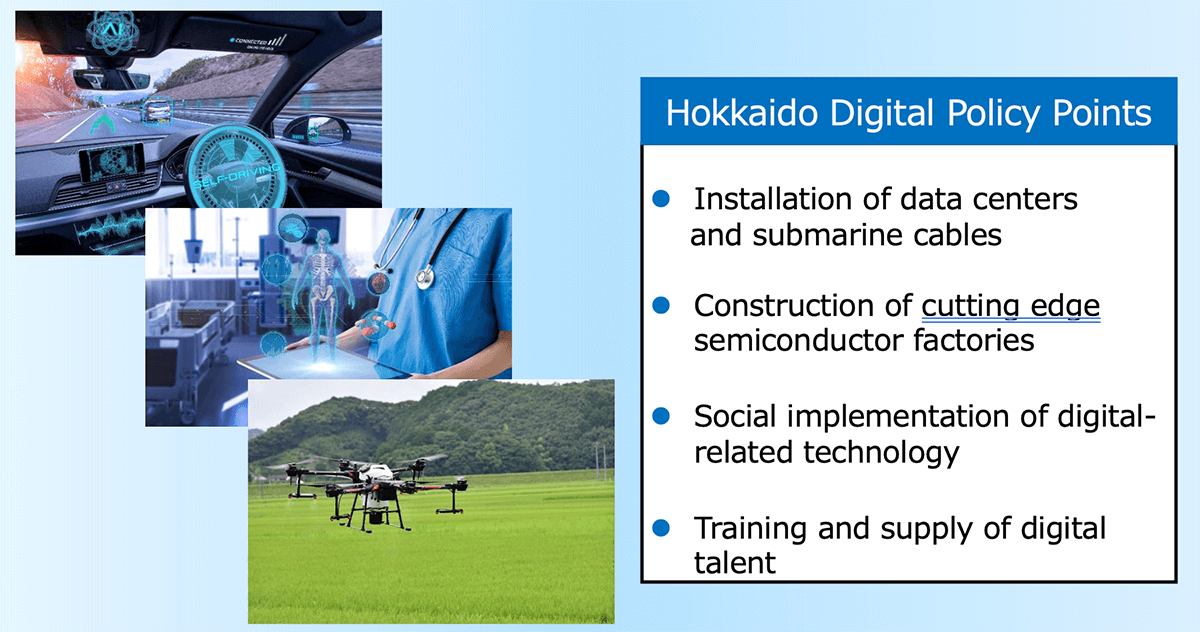
Direction of Hokkaido Digital Policies
- Currently coordinating the direction of digital policies going forward, preparing data centers and international submarine cables, utilizing renewable energy and the comprehension of the environmental change related to next-generation semiconductor manufacture.
デジタル関連産業の集積に向けた推進方向 令和5年(2023年)7月18日公表
https://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/kz/ssg/160226.htmlHokkaido’s Advantages
Capitalizing on the proximity to North America and Europe to create a data center and telecommunications network gateway
Hokkaido is in an ideal location to establish a low-latency network with Europe and North America.
Due to the melting of Arctic ice in recent years, it has become possible to lay submarine fiber-optic cables in the Arctic Ocean. Hokkaido, the northernmost point of Japan, can now be connected by shorter distances not only to North America, but Northern Europe as well. Until now, only KDDI and NTT Communications have installed international submarine fiber-optic cables north of Tohoku. But if Hokkaido, which is even further north, can attract the landing of international submarine cables from North America and Northern Europe, it will be home to data centers that are competitive on the global market and become an information distribution hub for the world.
Below are several concepts and proposals developed by private companies and researchers.
Contribution as a Domestic and International Digital Telecommunications hub
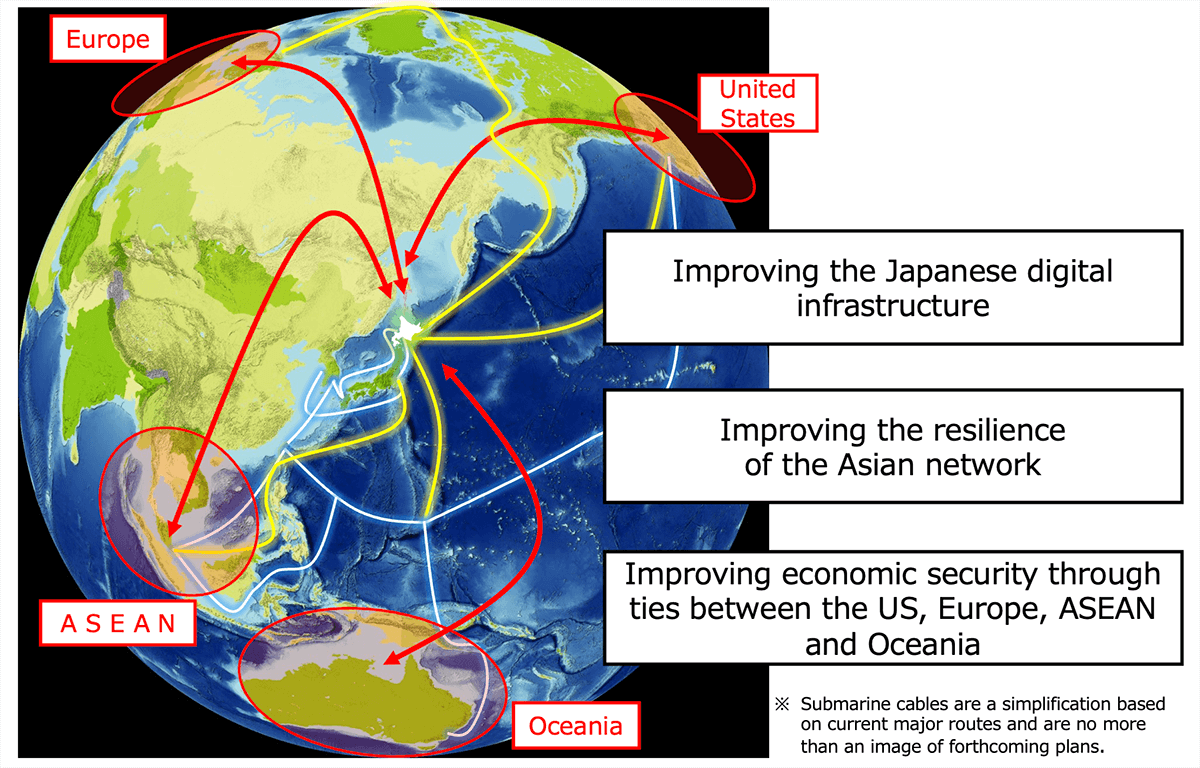
Domestic & International Network: Submarine Cables
- Hokkaido is working to strengthen its domestic and international submarine cable connections.
- When it comes to laying new international submarine cables, Hokkaido is geographically the closest Asian region to North America and Europe.
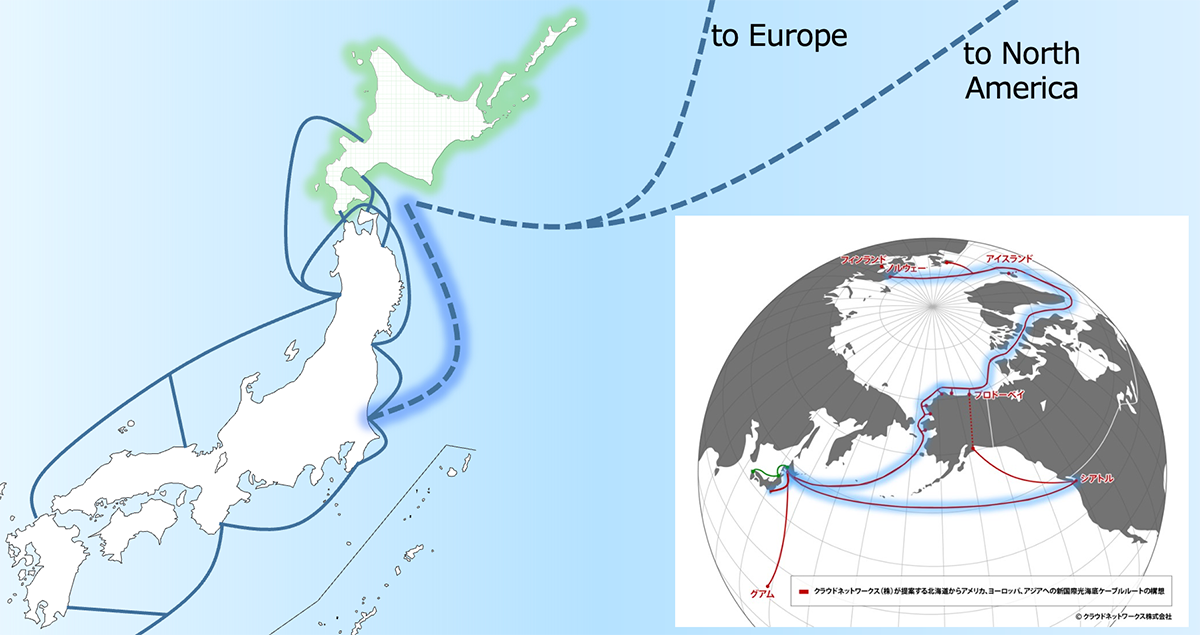
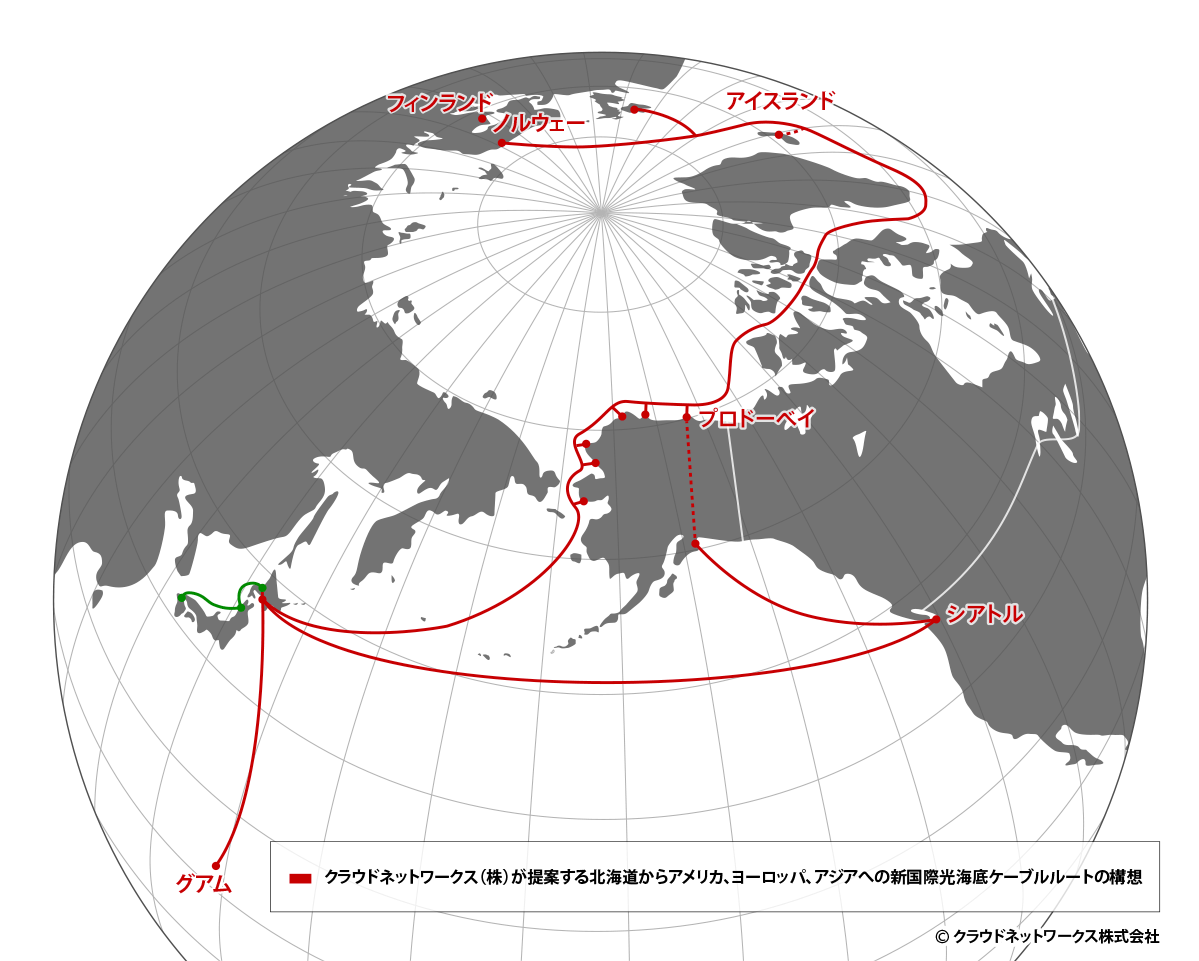
Arctic Ocean Cable Plan
Shortening the distance of fiber-optic transmission between Asia and Europe, reducing latency to the lowest possible amount
ARTERIA Networks Corporation and Finnish telecommunications company Cinia Ltd. are collaborating on a project (Far North Fiber, FNF) to lay submarine fiber-optic cables in the Arctic Sea to connect Asia and Europe.
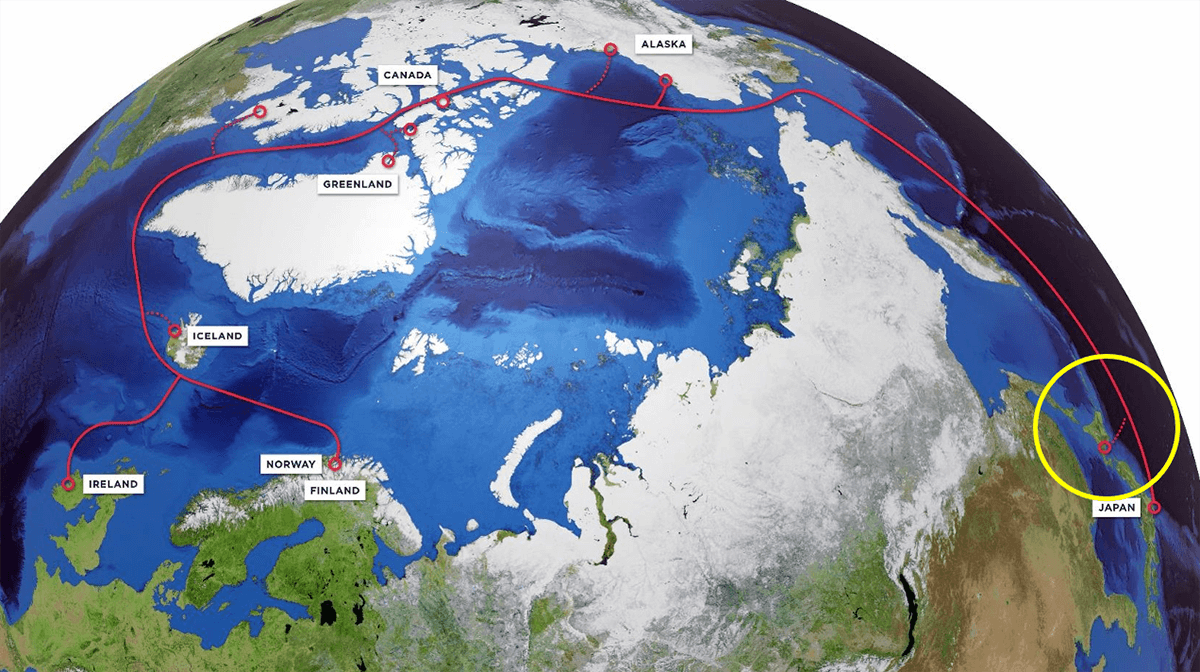
The FNF project aims to establish a new network of submarine fiber-optic cables between Japan and Europe. It plans to land cables in Alaska and the Canadian Arctic via the Northwest Passage in the Arctic Ocean, and in Norway or Finland and Ireland in Europe. The submarine cable system will span a total of 14,000 kilometers, shortening the distance of fiber-optic transmission between Asia and Europe and reducing latency to the lowest possible amount.
Attracting International Submarine Cable Projects
- Finland’s state-owned telecommunications company Cinia Ltd, Japan’s Arteria Networks Corporation and Alaska’s Far North Digital, LLC are working together on a Hokkaido submarine cable project, due for completion in 2026. Hokkaido is a candidate for a cable landing station.
- The European Commission will support this project with regard to economic security.
 Source:Cinia press release
Source:Cinia press release
Hokkaido’s Connection to the World
Excerpt from the Hokkaido Nutopia Datacenter Study Group’s Proposal
A digital Japan will not be born on accident. The most important piece of infrastructure for the establishment of Japan’s Society 5.0 form is a resilient, high-speed, large-capacity internet network and data centers. Industry, academia, and government must share specific plans and cooperate in order to realize this. Demonstrating this basic concept, Hokkaido will contribute to the Digital National Axis, which is made of submarine fiber-optic data transmission cables running along the Sea of Japan and Pacific Ocean sides of Japan, and a central data transmission line and data center bases across the Japanese archipelago. It will also establish submarine fiber-optic cable landing stations (digital freeports) in the Ishikari and Tomakomai areas, connecting Hokkaido to the rest of the world.
- Increase internet traffic from Hokkaido
- Disperse Japan’s internet between Hokkaido, Tokyo, and Osaka
- Must attract and gather related industry for implementation
Hokkaido Nutopia Datacenter Study Group
https://nutopia-hokkaido.org/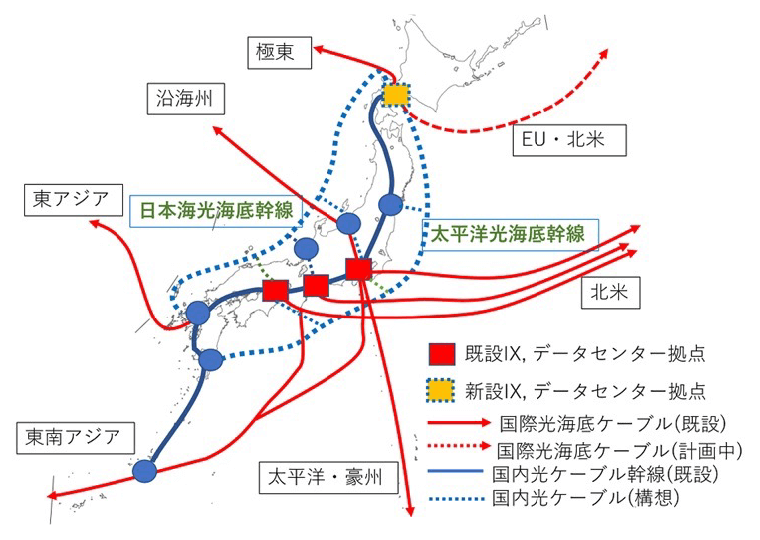 IX: abbreviation of internet exchange, connection point for ISPs (internet service providers)
IX: abbreviation of internet exchange, connection point for ISPs (internet service providers)Source: Hokkaido Nutopia Datacenter Study Group
Hokkaido’s Undertaking
Growing from a core base in Japan to a base in Asia
Hokkaido will serve as the data center, network, and hub connecting Asia to North America and Europe.
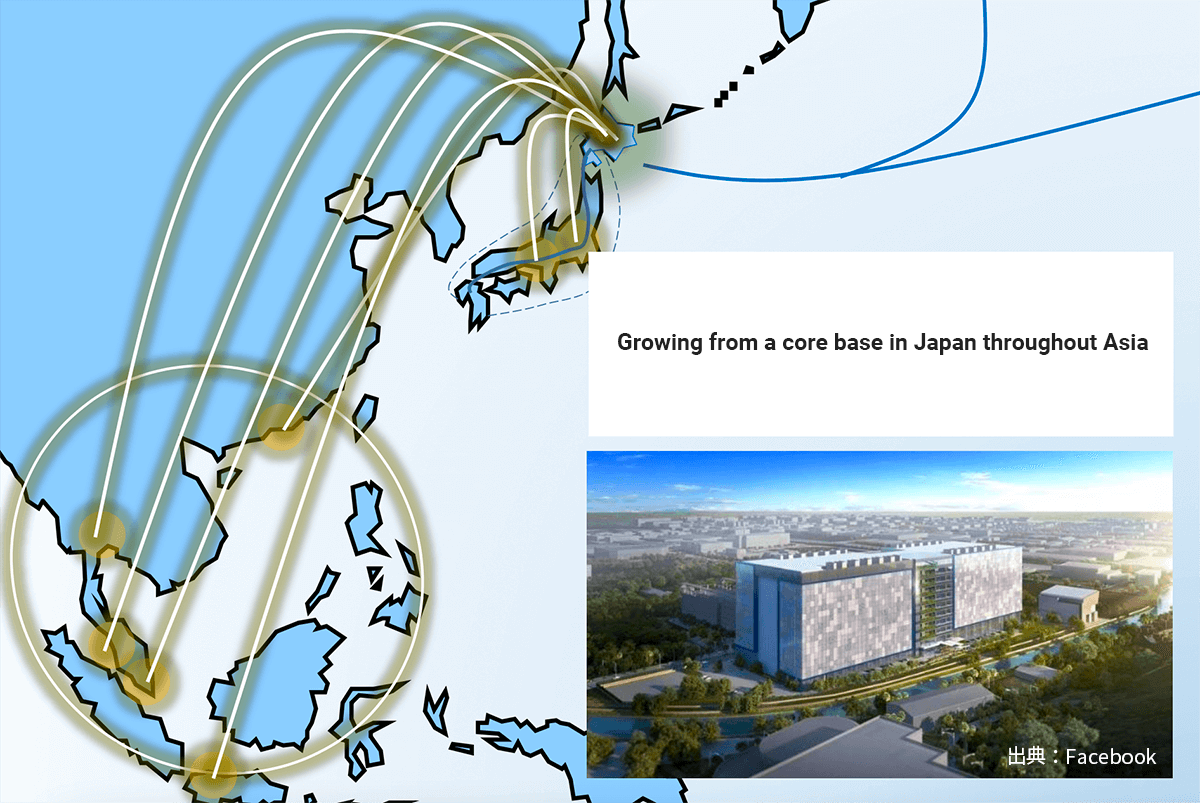
As Hokkaido is one of few regions in Asia with a subarctic climate and low average temperatures, its role in the data center industry will grow more and more important.
Also, with the ease of laying submarine cables due to its proximity to other countries, it has the potential to become the data center, network, and hub connecting Asia to North America and Europe.
Contact
-
Contact by Phone
Hokkaido Economic Affairs Bureau Industrial Promotion Division Location Promotion Section
011-204-5328(Japanese only)
-
Contact via Form

